Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) is a medical emergency that occurs when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the brain and other vital organs is disrupted, which can cause brain damage or death if not treated immediately.
SCA can happen to anyone, regardless of age or gender, but it is most common in people with underlying heart conditions or other health problems. Symptoms of SCA may include sudden loss of consciousness, absence of breathing, and lack of pulse.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest is different from a heart attack, which occurs when a blockage in the blood vessels that supply the heart with oxygen causes damage to the heart muscle. However, a heart attack can sometimes lead to Sudden Cardiac Arrest if it is not treated promptly.
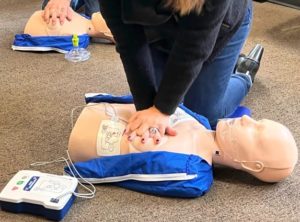
Immediate treatment for SCA is critical, and typically involves cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to help restore the heart’s normal rhythm, along with the use of an automated external defibrillator (AED) to shock the heart back into a normal rhythm. Each minute of defibrillation delay significantly decreases the person’s chance of survival.
The role of the Defibrillator in Sudden Cardiac Arrest
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a medical device used to treat sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). The AED works by delivering an electric shock to the heart, which can help to restore its normal rhythm.
When the AED is turned on, it will provide audio and visual instructions to the user, which will guide them through the process of attaching the electrode pads to the chest of the person in sudden cardiac arrest. Once the pads are attached, the AED will analyze the person’s heart rhythm to determine whether a shock is necessary.
If the AED detects an abnormal heart rhythm that can be corrected with a shock, it will charge up and prompt the user to stand clear. Once everyone is clear, the AED will deliver a shock to the person’s heart.
The shock is intended to temporarily stop the heart so that it can restart with a normal rhythm.
After the shock is delivered, the AED will continue to analyze the person’s heart rhythm and provide further instructions if necessary. If the person’s heart rhythm does not respond to the shock, the AED will continue to guide the user through the process of performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) until medical help arrives.
First Aid Oz delivers Nationally Recognized First Aid courses and CPR refresher training across Australia to individuals and industry groups.
Has your First Aid Certificate or CPR certificate expired or do you need First Aid for work or insurance ?
We can come to your workplace, school or sporting club, or you can come to one of our regularly scheduled classes.
Units we deliver include:
- HLTAID011 Provide First Aid
- HLTAID009 Provide Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
- HLTAID012 Provide First Aid in an education and care setting

Copyright 2023
First Aid Oz is a trading name of Global Fitness Institute (RTO 21793)
Delivering Nationally Recognized First Aid Courses across Australia